Assignemnt #53 Randomness
Code
/// Name: Jake Johnson
/// Period: 7
/// Program Name: Randomness
/// File Name: Randomness.java
/// Date Finished: 12/1/2015
import java.util.Random;
public class Randomness
{
public static void main ( String[] args )
{
Random r = new Random(); //changing this number effects how the random numbers are calculated (always the same in this case)
int x = 1 + r.nextInt(10);
System.out.println( "My random number is " + x );
System.out.println( "Here are some numbers from 1 to 5!" );
System.out.print( 1 + r.nextInt(5) + " " ); //removing the 1 makes the range of the numbers from 0 to 4
System.out.print( 1 + r.nextInt(5) + " " ); //this means that java starts the range of numbers at 0 and goes up 5
System.out.print( 1 + r.nextInt(5) + " " ); //adding 3 to this will make the range from 3 onwards
System.out.print( 1 + r.nextInt(5) + " " );
System.out.print( 1 + r.nextInt(5) + " " );
System.out.print( 1 + r.nextInt(5) + " " );
System.out.println();
System.out.println( "Here are some numbers from 1 to 100!" );
System.out.print( 1 + r.nextInt(100) + "\t" );
System.out.print( 1 + r.nextInt(100) + "\t" );
System.out.print( 1 + r.nextInt(100) + "\t" );
System.out.print( 1 + r.nextInt(100) + "\t" );
System.out.print( 1 + r.nextInt(100) + "\t" );
System.out.print( 1 + r.nextInt(100) + "\t" );
System.out.println();
int num1 = 1 + r.nextInt(10);
int num2 = 1 + r.nextInt(10);
if ( num1 == num2 )
{
System.out.println( "The random numbers were the same! Weird." );
}
if ( num1 != num2 )
{
System.out.println( "The random numbers were different! Not too surprising, actually." );
}
}
}
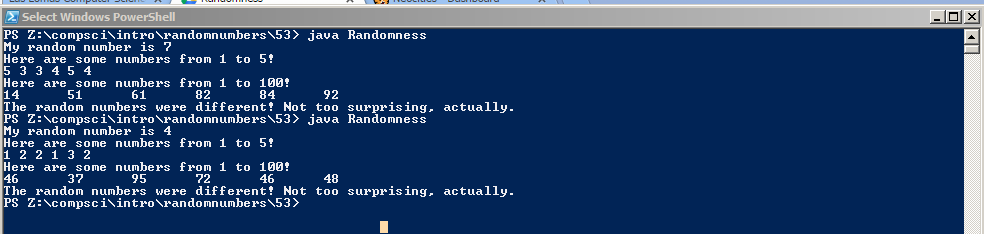
Picture of the output